|
|
|
 |
|
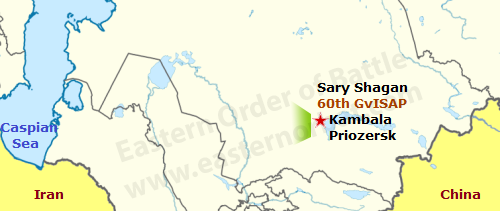
The Soviet Union built a new anti-ballistic and air defense missile testing field between 1958 and 1961 next to Lake Balkhash in the Kazakh SSR. This is where the 10th State Research and Testing Site was founded and the subordinate 60th Mixed Test Air Division.
|
|
The 60th Mixed Test Air Division's main tasks over the Sary Shagan test range:
- Supporting the anti-ballistic missile forces
- Supporting the air defence missile forces
- From 1965 supporting the air defence fighter aircraft live shooting training
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
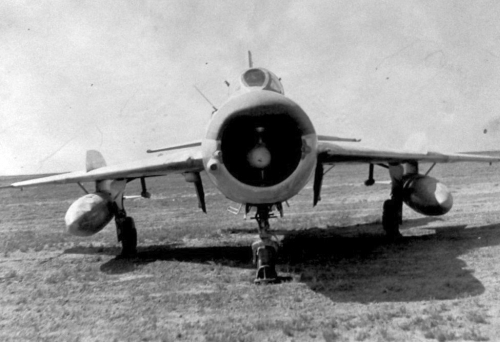
The main task of the 678th Guards Mixed Test Air Regiment was to operate remote-controlled drones and airborne target missiles. In the first half of the sixties used M-15 (MiG-15) ‘Fagot’, M-28 (IL-28) ‘Beagle’, M-16 (Tu-16) ‘Badger’ and supersonic speed M-19 (MiG-19) ‘Farmer’ remote-controlled drones. Used M13-1 target missiles and paratrooper target bomb too. For example, in 1963 the 678th regiment launched twenty-five target aircraft.
|
|
 |
|
Soviet research institutes here tested the new air defense weapon systems. Also, the fighter air units and anti-aircraft missile regiments of the Soviet Air Defense Force arrived here for missile shooting and complex air defense combat training
|
 |
 |
|
Soviet M-19 (MiG-19) Farmer remote target drone at the Kambala airfield
|
 |
 |
|
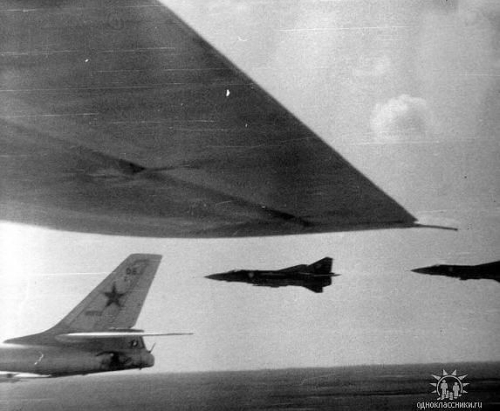
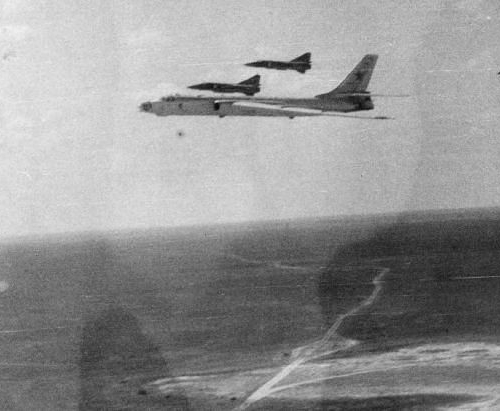
The 60th air division used the large Tu-16 ‘Badger’ bomber type as an observer, controller aircraft, MV-1(KSR-2 AS-5) Kelt target missile carrier or trarget drone.
|
 |
|
The regiment used older MiG-17 ‘Fresco’ observer aircraft and Tu-16 ‘Badger’ remote controller aircraft. From 1965 the 678th Guards Regiment received MiG-21F-13/U ‘Fishbed-C/Mongol-A’ support aircraft. This fighter was able to fly at 50 meters with high speed and simulated the maneuvering enemy forces.
|
 |
 |
|
The 678th Guards Mixed Test Air Regiment used the MiG-21F-13 ‘Fishbed-C’ support aircraft type until the late seventies.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
The flight crew perfectly mastered the handling of the drone technique by the end of the sixties. The engineering and technical staff began to confidently and reliably prepare target aircraft for flying and combat use. The combat control officers and radar operators gained a lot of experience in the handling of the drone technique.
Along with solving the problems of aviation testing support in the 60s, parts of the division paid great attention to the work on equipping technological facilities and utility rooms, improving the material base, the residential town, and creating normal living conditions for personnel.
|
 |
|
The seventies:
|
 |
|
Due to the development rapidity of electronic warfare equipment in the late sixties, the NATO enemy forces changed the tactics of air strikes. The electronic combat came to the forefront. The 60th Mixed Test Air Division received Yak-28PP ‘Brewer-E’ electronic countermeasures aircraft and An-12PP electronic countermeasure (ECM) aircraft in the early seventies. The division their own Tu-16 ‘Badger’ are equipped with ECM system too.
The 60th air division's person has used these ECM systems during test missile shootings from the early seventies.
|
 |
|
The first M-17 (MiG-17) ‘Fresco’ target drone aircraft arrived to Kambala-Priozersk airport in the early seventies. The M-17 (MiG-17) ‘Fresco’ type replaced the M-28 (IL-28) ‘Beagle’ and M-15 (MiG-15) ‘Fagot’ drones in the seventies. In 1971 the Kambala-Priozersk airport received the RSBN-2 short-range navigation system.
The 678th regiment's crew first launched M-17 (MiG-17) ‘Fresco’ target aircraft in pairs in 1973.
|
 |
|
In the seventies, the 60th Mixed Test Air Division often supported the research development of the Soviet Air Defence Force too. For example, during the Soyuz-74 research development exercise, the 678th Guards Mixed Test Air Regiment launched eight remote-controlled drones and 16 target missiles.
|
 |
|
In the late seventies and early eighties, the 678th Guards Mixed Test Air Regiment replaced their older technique to new high-speed support aircraft and airborne target missile/aircraft type. In 1977 the 678th guard air regiment received KSR-5NM (KSR-5 AS-6) ’Kingfish’ airborne target missile and low-flying, maneuvering capable M-17MNV (MiG-17) ‘Fresco’ drone aircraft type.
The first MiG-21M ‘Fishbed-J’ export fighter-type arrived to Kambala-Priozersk airport in 1979. (possibly arrived from the Krasnodar Flight Officers' School after the industrial overhaul maintenance)
|
|
|
 |
In the eighties, simulations of mass air strikes began at the complex combat training. For example, in 1982 the 678th Guards Mixed Test Air Regiment supported the research development of the new MiG-31 'Foxhound' interceptor. They launched four M-17 (MiG-17) 'Fresco' target drones at the same time. In the same year, they controlled more KSR-5NM (KSR-5 AS-6) ’Kingfish’ parallel for the first time.
In 1983 one squadron MiG-23M ‘Flogger-B’ support fighter aircraft and the new M-21 (MiG-21) ‘Fishbed’ remote-controlled drone type arrived. In the Ukrainian maintenance center, the older MiG-21PF/PFS/PFM/S ‘Fishbed-D/F/J’ tactical fighter aircrafts were converted to M-21 (MiG-21) supersonic target drone from the beginning of the eighties.
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
Unfortunately, during the complex air defense combat training, catastrophes also occurred. For Example:
- A new Soviet Su-27 ‘Flanker-B’ interceptor fighter attacked M-21 (MiG-21) ‘Fishbed’ target drone with R-27 'AA-10 Alamo' medium-to-long-range air-to-air missile. But unfortunately, the ground controller guided him to the wrong side. Because of this failure, instead of the M-21 (MiG-21), he shot down a Tu-128 ‘Fiddler’. The old Tu-128 interceptor was crashed, the crew died.
- In 1990 the MiG-31 ‘Foxhound’ of the 174th Guard Fighter Air Regiment PVO from the Monchegorsk airport shot another MiG-31 interceptor.
|
 |
|
By the late eighties, the Soviet Air Defense’s Sary Shagan missile test range reached the peak. In 1987 the 678th Guards Mixed Test Air Regiment launched 38 target drone aircraft and 136 airborne target missiles during 1254 combat flew. For example, during the Shield-87 exercise launched 13 M-21 (MiG-21) ‘Fishbed’ and M-16 (Tu-16) ‘Badger’ target drone aircraft as well as 8 KSR-5NM (KSR-5 AS-6) ’Kingfish’ and 2 MV-1 (KSR-2 AS-5) ‘Kelt’ target missile.
|
 |
|
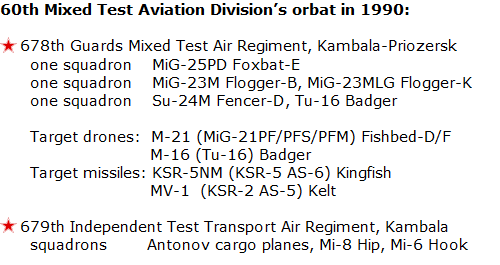
As the last development in 1990, the 678th Guards Mixed Test Air Regiment received one squadron high-speed MiG-25PD ‘Foxbat-E’ interceptor fighter planes from 738th Fighter Air Regiment PVO (from Zaporozhye airport Ukrainian SSR).
The 60th Mixed Test Air Division was terminated in 1994.
|
 |
 |
|
678th guard air regiment’s Tu-16 ‘Badger’ target missile carrier aircraft with special badges in the early nineties
|
 |
|
You might be interested in:
|
 |
|
Photos: Alexander Boltkov, Vladimir Kazantsev, Sergey Rolik collections
|
|